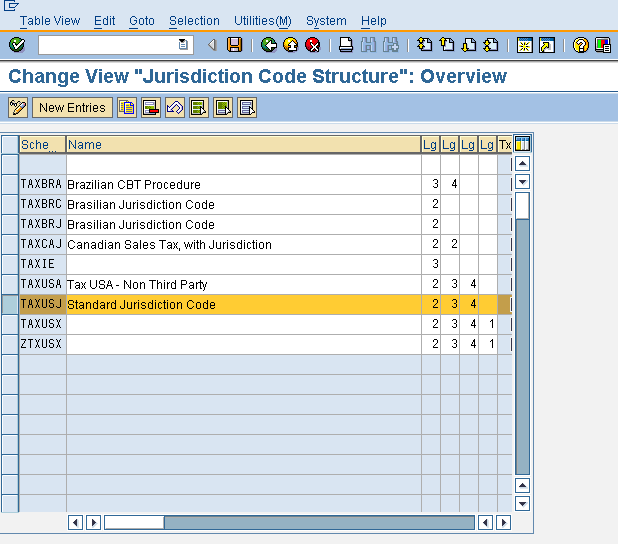
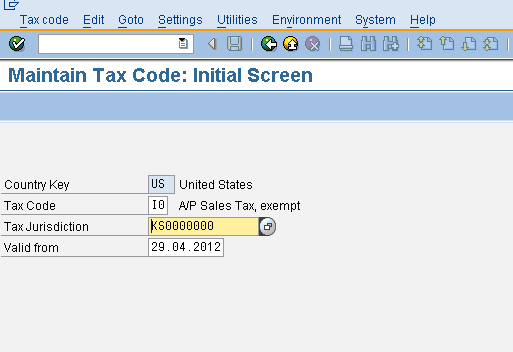
What is the difference between maintaining tax codes in TAXINJ and TAXINN
Both procedure TAXINJ and TAXINN has thin line difference where as TAXINN procedure is condition based & TAXINJ is fomula based.If you drag down details of TAXINJ is fomula based,where you can find Routine( selection with logic in line of condition type) are play vital role in tax calculation.
If you selected TAXINN procedure , you can maintained tax rate with respective condition types in FTXP during creation of tax code.But you should maintain condition record in FV11 t.code for condition types JMX1 & JMX2 are as 100%. Also you can maintain tax rate for condition types Basic Excise Duty,Edu cess , H. Edu cess,VAT/CST in FV11 t.code in stead of maintaining tax rate in FTXP.
1. TAXINJ is a tax calculation procedure for country version India and it supports formula-based excise determination. You need to configure this tax calculation procedure
Excise Conditions
⇒ JMOD IN: A/R BED
⇒ JNED IN: A/R NCCD
⇒ JAED IN: A/R AED
⇒ JSED IN: A/R SED
⇒ JCES IN: A/R Cess
⇒ JECS A/R Educational CESS
LST/CST/VAT Conditions
⇒ JIN1 IN: A/R CST
⇒ JIN2 IN: AR LST
⇒ JIN4 IN: A/R CST Surcharge
⇒ JIN5 IN: AR LST Surcharge
⇒ JIN6 A/R VAT Payable
⇒ JIN7 A/R CST Payable VAT
Service Tax Conditions
⇒ JSE4 Service Tax
⇒ JES4 ECS on Service Tax
2. Set up the following Account Key
IMG ⇒Financial Accounting ⇒ Financial Accounting Global Settings ⇒ Tax on Sales/Purchases ⇒ Basic Settings ⇒ Check and Change Settings for Tax Processing.
⇒ VS6 Input Tax
3. Define the Tax Procedure according to the settings in the figures below.
You can do this in the IMG ⇒ Financial Accounting ⇒ Financial Accounting Global Settings ⇒ Tax on Sales/Purchases ⇒ Basic Settings ⇒ Check Calculation Procedure ⇒ Define Procedures. Tcode:OBBG
4. Assign Tax Procedure to the country.
You can do this in the IMG ⇒ Financial Accounting ⇒ Financial Accounting Global Settings ⇒ Tax on Sales/Purchases ⇒ Basic Settings ⇒ Assign Country to Calculation Procedure. Tcode:OBYZ
The standard system comes with two tax calculation procedures. TAXINN is only supports condition-based excise determination, whereas TAXINJ supports condition-based excise determination and formula-based excise determination.
Both tax procedures contain condition types that cover all of the excise duties and sales taxes applicable.
Since the exact rates of excise duty can vary on a large number of factors, such as which vendor you purchase a material from, or which chapter ID the vendor stocks the material under, you create condition records for every sort of excise duty.
When you come to enter a purchasing document, the system applies the excise duty at the rates you have entered in the condition records.
Activities,
Customizing
Make the settings in Customizing for Logistics u2013 General, by choosing Taxes on Goods Movements ⇒ India ⇒ Basic Settings ⇒ Excise Duties Using Condition Technique and u2026 ⇒ Account Determination.
These activities include one activity where you define a tax code for condition-based excise determination.
Master Data
Create condition records for all excise duties that apply, and enter the tax code for condition-based excise determination in each.
TAXINN Vs TAXINJ:
Definition: condition-based excise determination
A method that the system uses of determining excise duty in India.
This method requires you to create condition records for each combination of vendor or customer and material (and possibly other conditions).When you create a purchasing document, the system calls the tax procedure assigned to India. The tax procedure finds all of the condition records that you have created for that combination of vendor and material.
When you create a sales document, the excise duties and sales taxes are determined by the pricing procedure (not the tax procedure).
Definition: formula-based excise determination
A method that the system uses of determining excise duty in India.
This method was used in the Country Version India Add-On and requires you to maintain additional data in the Excise Rate Maintenance transaction, J1ID.
When you create a purchasing document, the system calls the tax procedure assigned to India. Each of the excise duties in the tax procedure has its own condition types, and each condition type is assigned to a formula. This formula instructs the system to calculate the excise duty using the data that you have maintained in the Excise Rate Maintenance transaction.
When you create a sales document, the system determines the excise duties and sales taxes using the pricing procedure (not the tax procedure).
Pricing Procedures:
The primary job of a pricing procedure is to define a group of condition types in a particular sequence. The pricing procedure also determines:
- Which sub-totals appear during pricing
- To what extent pricing can be processed manually
- Which method the system uses to calculate percentage discounts and surcharges
- Which requirements for a particular condition type must be fulfilled before the system takes the condition into account
Example of a Pricing Procedure:
If a sales department processes sales orders for a variety of foreign customers, the department can group the customers by country or region. A pricing procedure can then be defined for each group of customers. Each procedure can include condition types that determine, for example, country-specific taxes. In sales order processing, you can specify pricing procedures for specific customers and for sales document types. The system automatically determines which procedure to use.
Choose Basic Functions ® Pricing ® Pricing control ® Define and assign pricing procedures.
Assign Pricing Procedure to Sales Area
T Code: OVKK and assign respective sales area for different kind of pricing procedure.
Pricing procedure follows below assignment.
Pricing procedure ⇒ condition types(1:N) ⇒ access sequence (1:N) ⇒ accesses(1:N) ⇒ condition tables(1:1) ⇒ condition fields.
During creation you can follow bottom-up sequence.
1. Create condition table with condition fields. CUSXXXXX
2. Create access sequence and maintain accesses assigned with condition table. ZAS ->CUSXXXXX
3. Create condition type and assign access sequence. ZCT->ZAS
4. Create pricing procedure and assign condition types. ZPP->ZCT
Determination part.
In order to determine pricing procedure 5 parameters needed.
Sales org + distribution channel + division + customer pricing procedure + document pricing procedure ,SO+DC+DIV+CP+DP = ZPP
and we assign pricing procedure against above 5 parameters in the configuration.
based on condition maintenance we restrict the application where you gonna maintain the condition record.
lets say you restricted it to product and successfully you maintained a condition record for testing.
now I am using this product in a transaction document(example ZAG). you called the transaction type(ZAG) and entered the customer ABC and entered some product XYZ with quantity. now the minute you enter the product and hit on enter.
System searches for relevant pricing procedure to determine. by formulating all 5 parameters from the sources based on org model it brings respective sales area data(SO+DC+DIV) and based on ABC’s customer pricing procedure(you can find it in sales area data a/block under billing area.
based on transaction type it will bring the value document pricing procedure ( ZAG’s transaction category header data).
after forumalting all 5 parameters it determines corresponding pricing procedure from the configuration.
again based on the maintained condition record it will apply the value on to the screen.
based on number of different condition types(diff calculation types) it will show different price element in the output. and all these calculation will be done by IPC.